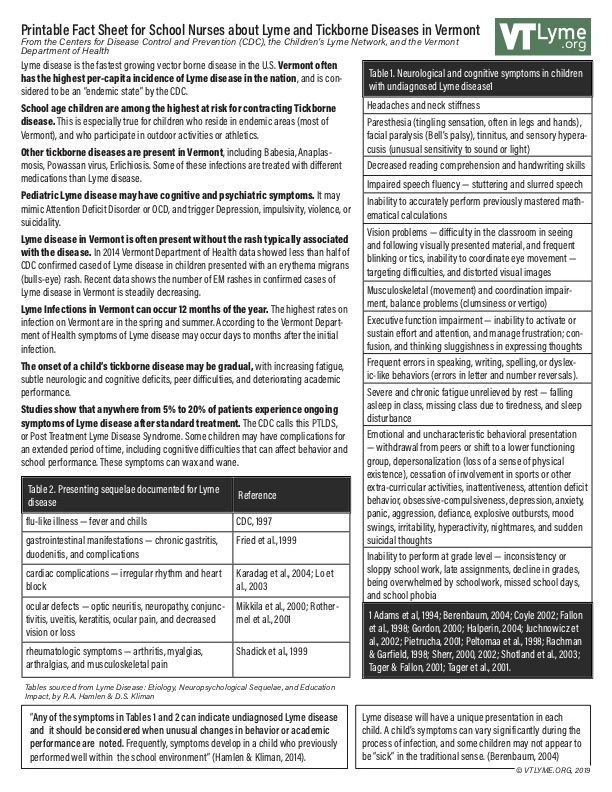
The rate of infections with B. burgdorferi and other tickborne pathogens are increasing in Vermont, and researchers are discovering new, previously unknown species that cause disease symptoms. Vermont has one of the highest incidence rates in the USA of Lyme disease, and our state needs more physicians skilled in the diagnosis and treatment of tickborne illnesses.
There are different treatment guidelines specific to Lyme disease in the U.S. Both are peer reviewed. The ILAD’s guidelines Evidence Assessments and Guideline Recommendations were created in 2014. New IDSA guidelines were published in 2020.
Here is an annotated appendix with comparisons of the IDSA and ILADS guidelines. (Note: This comparison uses an older version of the IDSA guidelines.)
Lyme disease may present as anxiety, or with non-specific symptoms. In December 2013 the CDC published a report on three sudden deaths caused by Lyme Carditis. Patient 3 “complained of episodic shortness of breath and anxiety during the 7–10 days before death. No rash, arthralgia, or neurologic symptoms were noted. A physician consulted 1 day before death prescribed clonazepam for anxiety.” Patient 1 “described a nonspecific illness with malaise and muscle and joint pain during the 2 weeks before death.” In 2018 the VDH and CDC announced the first confirmed death from Lyme Carditis in Vermont.
Symptoms of tickborne diseases can include insomnia and fatigue. A recent study on post-treatment illness showed a “strong correlation between sleep disturbance, fatigue, pain and anxiety, as well as sleep disturbance with cognitive complains”.
According to the CDC, in pregnant women untreated Lyme disease can lead to infection of the placenta, or be transmitted from mother to fetus.
Controversy and misinformation about Lyme diagnosis and treatment has left some Vermonters undiagnosed, undertreated, and vulnerable to long-term, preventable, health problems from Lyme disease and other tickborne infections. Currently, some Vermonters already sick from neurological, complex, or untreated infections travel hours, or out of state, to receive effective treatment.
The International Lyme and Associated Diseases Society (ILADS) offers a Physician Training Program. Their goal is to foster excellence in care for Lyme disease patients, addressing the challenges and changes in effectively diagnosing and treating tick-borne diseases. Scholarships are available.
Learn more about different perspectives on diagnosing and treating Lyme disease and other tickborne diseases.
To report a tickborne disease the Vermont Department of Health would like you to call them directly at 802-863-7240. The CDC also posts a Lyme Disease Case Report form online.